„Wir dachten, dass es weniger lange dauert“
 LUXEMBURG Flüchtlingshilfe:
LUXEMBURG Flüchtlingshilfe:
Bei vielen bürokratischen Prozessen ist Geduld gefragt
 LUXEMBURG Flüchtlingshilfe:
LUXEMBURG Flüchtlingshilfe:
Bei vielen bürokratischen Prozessen ist Geduld gefragt
 LUXEMBURG Flüchtlingshilfe:
LUXEMBURG Flüchtlingshilfe:
Bei vielen bürokratischen Prozessen ist Geduld gefragt
Je länger der Krieg in der Ukraine währt, desto größer wird die Notwendigkeit einer langfristig ausgerichteten Integrationspolitik. Wir haben mit Sérgio Ferreira, dem politischen Beauftragten der Association de Soutien aux Travailleurs Immigrés (Asti), über vergangene Fehler und aktuelle Herausforderungen gesprochen.
Stefan Kunzmann Revue 21.04.2022
Diskriminierung aufgrund von Herkunft und Hautfarbe ist
nach wie vor weit verbreitet – auch in Luxemburg, wie eine Studie belegt. Das zeigt sich auch bei der „Zweiklassenmigration“
im Umgang mit Geflüchteten.
RTL Background am Gespréich vum 23. Abrëll – Antonia Ganeto, Max Hahn a Sylvain Besch
E Samschdeg waren d’Spriecherin vu Finkapé, den DP-Deputéierten an de Responsabele vum CEFIS eis Invitéen an der Emissioun Background am Gespréich.
Et feelt un Ulafstellen fir sech géint Rassismus ze wieren, dat ass an eiser Emissioun Background am Gespréich iwwert de Rassismus hei am Land däitlech ginn. Invitée waren d’Antónia Ganeto, Spriecherin vun Finkapé, de Max Hahn vun der DP, President vun der Chambercommissioun fir Famill an Integratioun an de Sylvain Besch, Responsabele vum CEFIS a Co-Auteur vun enger Etüd iwwert de Rassismus zu Lëtzebuerg.
Dee Rapport mëscht däitlech, dass et och hei am Land e Problem mat Rassismus an Diskriminatioune gëtt. Deen sech virun allem a bestëmmte Beräicher weist, wéi den Co-Auteur vun der Etüd, de Sylvain Besch ervirgestrach huet:
Grouss Secteuren wéi d’Aarbecht, d’Schoul an d’Wunnen wiere besonnesch impaktéiert, wéi d’Etüd gewisen huet. Duerch déi qualitativ Approche vum CEFIS hätt een och déi verschidde Formen vu Rassismus gesinn. Ausserdeem war et och d’Zil vun der Etude ze kucken, wéi eng Gruppen vu Leit besonnesch vu Rassismus an/oder Diskriminatioune betraff sinn. Do hätt sech eraus gestallt, dass virun allem Leit mat enger schwaarzer Hautfaarf betraff sinn.
Doriwwer eraus och Leit, déi en arabeschen oder muslimeschen Hannergrond hunn, esou wéi och Persounen mat portugiseschen Originnen.
2/3 vun de Persounen, déi rassistesch diskriminéiert ginn, maachen awer keng Plainte. Och dat ass am Rapport ze liesen. D’Antónia Ganeto, Spriecherin vu Finkapé, kennt dat Phenomen:
Wann ee schafft, ass ee nämlech finanziell ofhängeg. Andeems ee géint säi Patron oder Virgesetzten virgeet, riskéiert ee vill. Bei Finkapé hätten sech scho mol Leit gemellt, déi wéinst hirer Hautfaarf diskriminéiert goufen a net wossten, wat si sollte maachen.
D’Aktivistin vu Finkapé huet och selwer eng Plainte wéinst sexisteschen a rassistesche Beleidegungen am Internet deposéiert, wat net einfach gewiescht wier, wéi si an eiser Emissioun soot. Den Täter gouf zu enger Geldstrof vun 1500€ verurteelt. An engem Gespréich mat der Antónia Ganeto hätt hien säi Feeler och net agesinn, esou nach d’Antónia Ganeto.
Den Hannergrond: beim Fraestreik am Mäerz 2020 gouf eng Foto vun der Antónia Ganeto gemaach, wéi si an e Megaphon schwätzt op deem e Sticker vu Richtung 22 war mam Sproch „Lëtzebuerg, du hannerhältegt Stéck Schäiss“ gepecht war. De Sticker, respektiv déi Ausso hat awer näischt mat der Ried vun der Antónia Ganeto ze dinn an si hat d’Pechbild och guer net bemierkt, wéi si de Megaphon kritt huet. Doropshin gouf awer rassisteschen an sexisteschen Hate Speech an de soziale Reseauen ausgeléist. Eng traumatiséierend Erfarung, wéi d’Aktivistin ënnerstrach huet.
Mat hirer Plainte hätt si virun allem wëlle weisen, dass et wichteg ass an d’Ëffentlechkeet ze goen an de Rassismus kloer ze weisen.
Et wier net un den Associatiounen eleng fir d’Leit opzefänken, mee et bréicht een och Institutiounen, déi dohannert stinn. Den Zentrum fir Gläichbehandlung CET huet net genuch Ressourcen oder Pouvoiren, fir d’Leit konkret bei Fäll vu Rassismus kënnen ze begleeden. Fir de Max Hahn, President vun der zoustänneger Chamberkommissioun fir Famill an Integratioun missten et verschidden Ulafstelle ginn, dorënner eben och den CET, fir deen elo Ännerunge virgesi sinn. Den DP-Deputéierten Max Hahn sot, dass de Wëllen do wier, wat een och an der Chamberdebatt iwwert de Rassismus gesinn hätt. An der Chamber gouf och eng Motioun gestëmmt, déi méi Ressourcen fir den CET virgesäit. Et goufen och scho nei Leit agestallt, fir deem gerecht ze ginn. Doriwwer eraus wier et awer och wichteg, de Leit ze kommunizéieren, dass et déi Ulafstell gëtt. An et misst ee kloer definéieren, wat alles als Diskriminéierung zielt.
Sensibiliséieren ass och der Antónia Ganeto wichteg. Woubäi si awer betount huet, dass e nationale Plang fir Integratioun dofir net duergeet. Et misst een de Problem beim Numm nennen an et bréicht een dofir e nationalen Aktiounsplang géint de Rassismus, deen konkret a gezielt Léisunge virgesäit.
Déi rezent Etüd vum CEFIS, dem Zenter fir interkulturell a sozial Studien a Formatiounen an dem Liser, dem Zenter fir sozio-ekonomesch Recherche wier sécher eng Chance, fir eppes ze verbesseren, seet d’Antonia Ganeto vu Finkapé. Se wierklech ze bewäerten, wär awer schwiereg, well se nach net den Experte virgestallt gouf. Allgemeng misst méi op Sensibiliséierung gesat ginn, fir dass sech Saache verbesseren. Déi dräi Invitée waren sech dann och eenz, dass de Rapport net dierft am Tirang verschwannen. Elo wou een Zuelen hätt, wier et wichteg weider ze kucken, wéi d’Etüd kann hëllefen fir géint de Rassismus zu Lëtzebuerg virzegoen.
Schoulufank fir ukrainesch Kanner zu Lëtzebuerg 100komma7 19. Abrell 2022
Dës Hëllefsorganisatioune sammele Spenden RTL
Interview de Nadine Conrardy et Rémi Fabbri de la Croix Rouge dans le Quotidien du 19 avril 2022
Op Besuch am ukraineschen Haus zu Stroossen 100komma7 19. Abrell 2022
Aus fünf mach 21 : Wie eine Familie aus Contern Flüchtlinge aus der Ukraine aufgenommen hat
Luxemburger Wort 12. März 2022
„Kyjv“ statt „Kiew“ – eine Frage der Identität
UKRAINE-KRIEG Luxemburger nimmt vierköpfige Flüchtlingsfamilie auf
„Kyjv“ statt „Kiew“ – eine Frage der Identität
UKRAINE-KRIEG Luxemburger nimmt vierköpfige Flüchtlingsfamilie auf
Ein Kinderlächeln, eine Tasse Kaffee und Frieden
Luxemburger Wort 12. April 2022
Luxemburger Wort 12. April 2022
Von den Schwierigkeiten und Hindernissen der Flüchtlinge aus der Ukraine im Zugang zum Arbeitsmarkt, trotz freiem Zugang
Luxemburger Wort 15. April 2022
Les Ukrainiens pourraient avoir du mal à trouver un emploi
Sur le parking avenue Kennedy au Kirchberg, à côté du Parlement européen des tentes vont bientôt servir de premier accueil pour les réfugiés.
Voici des phots des bénévoles à l’oeuvre ce dimanche pour finaliser les installations



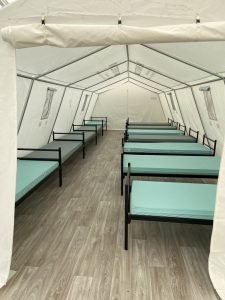
Réfugiés: l’adaptation à marche forcée des infrastructures d’accueil
IPS JOURNAL Europe April 8, 2022
What’s next for African and Asian war refugees?
African and Asian students who fled the war in Ukraine face not just the racism of Europe’s refugee policy, but also an uncertain educational future
Emmanuel Achiri & Hrishabh Sandilya
African and Asian students who fled the war in Ukraine face not just the racism of Europe’s refugee policy, but also an uncertain educational future Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has created an unprecedented humanitarian and refugee crisis in Europe, not seen since World War II, classified by the UNHCR as a level 3 emergency – the highest level available. Over 4 million refugees – mostly women, children, and students – have fled Ukraine over the past month. In response, Europe has opened its arms to Ukrainian refugees and the EU has announced that all Ukrainians are eligible for temporary refugee protection for up to three years, with politicians and the public showing their support. This is how the international refugee protection regime should work.
According to official Ukrainian government statistics, Ukraine had over 76,000 foreign students in 2020. About 20,000 of these were Indians and over 15,000 originated from Africa, mainly from Nigeria, Morocco, and Egypt. In contrast, they have had a very different experience fleeing Ukraine. African and Asian students have described horrid stories of them being beaten with sticks by Ukrainian security, pushed off buses and trains, and neglected in favour of Ukrainians. And recent disturbing reports suggest that they are also being unfairly detained at EU borders – being denied access to protection, basic human rights, and dignity, as well as being threatened with deportation. This xenophobic separation between white and non-white refugees is alarming. It has been referred to as selective-restricted access to EU refugee protection based on the politicisation of the right to asylum resulting in a de facto abolishment of the right to seek protection.
The racism and double standards inherent in Europe’s response to refugee crises are obvious and glaring. Kiril Petkov, Prime Minister of Bulgaria, couldn’t have been more transparent about the double standard. ‘These are not the refugees we are used to. … These people are Europeans. … These people are intelligent; they are educated people. … This is not the refugee wave we have been used to, people we were not sure about their identity, people with unclear pasts, who could have been even terrorists’.
Every refugee deserves protection
Refugees are vulnerable. Colour, race, or nationality should not matter at all. Such blatant racism is not only unacceptable, but further threatens the health and lives of refugees. Fleeing the violence of war, refugees struggle to access clean water, food, shelter, and quality health care. Racial trauma only causes them more physical and mental harm. This vulnerability is worsened for students fleeing war, who are often very young, far away from their families and support networks, and may not have enough financial resources. One of the reasons why Ukraine hosts so many students from the Global South is due to the affordability of its universities.
What does the future for the African and Asian students who were at Ukrainian universities look like?
Many African and Asian students in Ukraine have ended up leading their own rescue efforts: assisting with transportation to borders, navigating others to bunkers, and offering different types of support. Volunteers suggested this was ’because there was a gap in the access Black and Brown people were getting.’ Some African and Asian countries took steps to ensure their nationals could enter EU member states and organised transport home but many thousands had to deal with the situation themselves. While data on the number of African and Asian students still stuck in Ukraine is scarce, reports about students requesting for evacuation and green corridors continue to emerge. Clearly, there are foreign students who have been unable to make it out so far, and some may have lost their lives too.
What does the future for the African and Asian students who were at Ukrainian universities look like? First, for those who wish to stay in Europe or cannot be repatriated back to their home countries, what comes next as they seek to rebuild their lives, study further and apply for asylum themselves? And second, for those who have indeed returned home, how can they reintegrate into their societies and perhaps more importantly, restart their education and/or switch to professional careers?
The students’ future
For those who wish to stay in Europe, the EU’s temporary protection directive will not uniformly apply to students who did not have permanent residency in Ukraine before the war, and instead they must apply for asylum at a national level if they seek protection. It is yet unclear if member states will grant asylum this way. And if past refugee waves have told us anything, it is that Africans and Asians are at a significant disadvantage.
For the large number of those who have returned home, the question about their educational and professional future now
In response to widespread criticism, another route is emerging in which students could possibly transfer their studies to another European country. So far, France has suggested that some Africans studying in Ukraine may continue their studies at French universities. This project, driven by arises. the Presidential Council for Africa (CPA), would allow Africans fluent in French find a university offering the same curriculum to enrol in France. Hungary has also announced that some Ghanian students will be allowed to finish their studies at its universities but it is still unclear which students are eligible. While one hopes that other EU members follow suit, the racist response of countries like Estonia, which is making special exemptions for Ukrainian students to enter universities in the middle of the year, but not foreign students who were in Ukraine, is a reality check. It would thus be prudent for student refugees to ally with European student organisations and lobby for politicians to do more.
For the large number of those who have returned home, the question about their educational and professional future now arises. For many, the main concern is how to finish their education – especially for those close to completion.
In Nigeria, the fear is that students who have returned to the country will be unable to acquire the requisite visas and financial means to study elsewhere in Europe. Others have expressed doubts about the quality of education in Nigeria and hope to return to Ukraine or migrate elsewhere, despite private Nigerian universities waking up to the opportunity that these returning students may present.
In India, most students who have returned from Ukraine are studying medicine. While the Indian Medical Association has recommended they be allowed to join programmes in India to finish up, doubts remain over whether this is feasible for all of them given the intense domestic competition and limited seats available for medical studies. Other issues, including lateral transfers of credits and the need for rehabilitation have also been raised, with no clear path forward emerging – as yet.
The current degrading and inhumane detention practices of African and Asian student refugees at European borders need immediate rectification.
The situation is marginally better in South Africa, following consultations between students and university representatives. Despite the difficulties this might pose, some universities have begun drawing up proposals to integrate fifth- and sixth-year medical students. On the other hand, Cameroonian authorities have been largely silent on the futures of returning Cameroonian students, whilst calling for peace and dialogue between Russia and Ukraine.
Europe can and must do more
Clearly, there are more questions than answers at this stage. And while Europe’s current focus is on the humanitarian situation on its borders with Ukraine, this focus will inevitably shift to matters of integration. Hopefully, innocent foreign students are not bogged down in EU member states’ notoriously slow decision-making processes and policy- makers and universities can rise to the occasion instead.
While France and Hungary’s approach is a start, there is still the need for a concerted effort to ensure that these students are able to continue their studies without losing years of effort, learning and tuition fees. These students, many of whom will probably seek asylum in the coming months, need to be provided not only with international protection, but also academic opportunities. Thus, EU member states should recognise the vulnerability of student refugees and embrace and offer them the opportunity to transfer to European universities, in circumstances devoid of the rigid and racially motivated rules which prioritise some refugees as more deserving than others.
The current degrading and inhumane detention practices of African and Asian student refugees at European borders need immediate rectification.
European leaders must live up to their commitments on international protection guaranteeing them to all, irrespective of race, colour, nationality, or ethnic origin by offering humanitarian assistance to these student refugees.
Similarly, African and Asian governments must begin much-needed discussions with local universities, professional bodies, and student associations to ensure that those who have returned home are equally able to continue their studies – and rebuild their academic and professional lives.
Capacités d’hébergement, traitement des dossiers, statut des différents cas : l’arrivée massive en un laps de temps très court de réfugiés ukrainiens (4 000 selon le dernier décompte et environ 2 000 demandes introduites depuis l’étranger), soulève de nombreuses questions d’ordre pratique et juridique.
Le Collectif Réfugiés (Lëtzebuerger Flüchtlingsrot, ou LFR), qui regroupe des associations veillant au respect des droits des réfugiés, a donc sollicité une entrevue avec l’Office national de l’accueil (ONA) et la direction de l’Immigration pour faire le point sur la situation. Elle a eu lieu le 25 mars.
«Une demande de protection temporaire, ce n’est jamais arrivé en Europe. Des concertations régulières avec les autorités vont donc être nécessaires et il va falloir du temps pour mettre les choses en place, car des questions seront soulevées au fur et à mesure que nous serons confrontés à différentes situations», prévient d’emblée Ambre Schulz, coordinatrice de projets pour l’association Passerell.
Parmi les problématiques déjà posées : quid des personnes fuyant l’Ukraine originaires de pays tiers? La réponse reste encore floue pour l’instant, mais devrait être précisée prochainement. La protection temporaire semble en effet pouvoir être accordée à ces personnes si elles ne peuvent «rentrer dans leur pays d’origine dans des conditions sûres et durables». «Mais quelles sont les conditions précises?», interroge Ambre Schulz, qui souligne que le cas ne s’est toutefois pas encore présenté au Luxembourg.
Autre point sur lequel le LFR a interpellé les autorités : le traitement particulier des dossiers. «Parmi les réfugiés ukrainiens, certains peuvent bénéficier du droit d’asile» et pas seulement d’une protection temporaire, explique Ambre Schulz.
Différence de traitement
Si le collectif salue la réactivité des autorités et la mise en place d’un guichet unique rassemblant tous les acteurs compétents pour l’accès à la procédure des personnes fuyant l’Ukraine, il enjoint aussi aux autorités de lancer un appel à projets pour soutenir les associations qui œuvrent en faveur de ces personnes, et à ne pas oublier les autres demandeurs de protection internationale (DPI), qui peuvent avoir le sentiment d’une différence de traitement.
«Il va falloir être vigilant, car la situation actuelle va forcément avoir un impact sur les autres procédures : les examens des dossiers et les vérifications habituelles vont être retardés, ce qui retardera d’autant l’accès aux documents des migrants, donc leur statut et leur intégration complète au Luxembourg», craint Ambre Schulz.
Le LFR déplore par ailleurs la reprise des assignations à résidence, à laquelle s’opposent depuis longtemps les associations pour lesquelles cette assignation n’est ni plus ni moins qu’une «restriction des libertés pour les personnes dans la procédure Dublin». Cette procédure permet d’établir le pays responsable de l’examen de la demande d’asile et peut donc impliquer un transfert de la personne.
Les demandeurs d’asile en procédure Dublin ont en effet été transférés de la Structure d’hébergement d’urgence (SHUK) vers la Wanteraktioun (WAK) pour laisser la place à l’accueil d’urgence des réfugiés ukrainiens. L’assignation à résidence avait donc été suspendue jusqu’au 1er avril. «Cela crée une différence de traitement entre les réfugiés, puisque ces DPI doivent obligatoirement rentrer le soir, mais en plus il s’avère que ces restrictions ont pu être très facilement et rapidement levées. On peut donc vraiment questionner leur nécessité», estime Ambre Schulz.
De même, les bénéficiaires de la protection temporaire peuvent accéder librement au marché du travail sans avoir besoin de solliciter une «autorisation d’occupation temporaire» (AOT). Une mesure qui «satisfait» le LFR, mais qui, là encore, crée une différence notoire entre réfugiés : les autres demandeurs de protection internationale doivent eux patienter six mois avant de pouvoir solliciter une AOT.
«Nous restons attentifs et vigilants face à l’appréciation qui sera faite concernant les demandes de protection pour les personnes fuyant la guerre en Ukraine et les demandeurs de protection internationale qui fuient la persécution et qui se trouvent déjà au Luxembourg», annonce le LFR.
Davantage d’hébergements
Dans sa réponse à la question parlementaire n° 5730, le gouvernement a annoncé prévoir en 2022 l’ouverture de six structures d’hébergement temporaires pour demandeurs de protection internationale (SHTDPI) avec un total de 466 lits, hors structures d’urgence dans le contexte de la guerre en Ukraine, qui sont au nombre de 19 à l’heure actuelle.